# LockSupport
## 原理
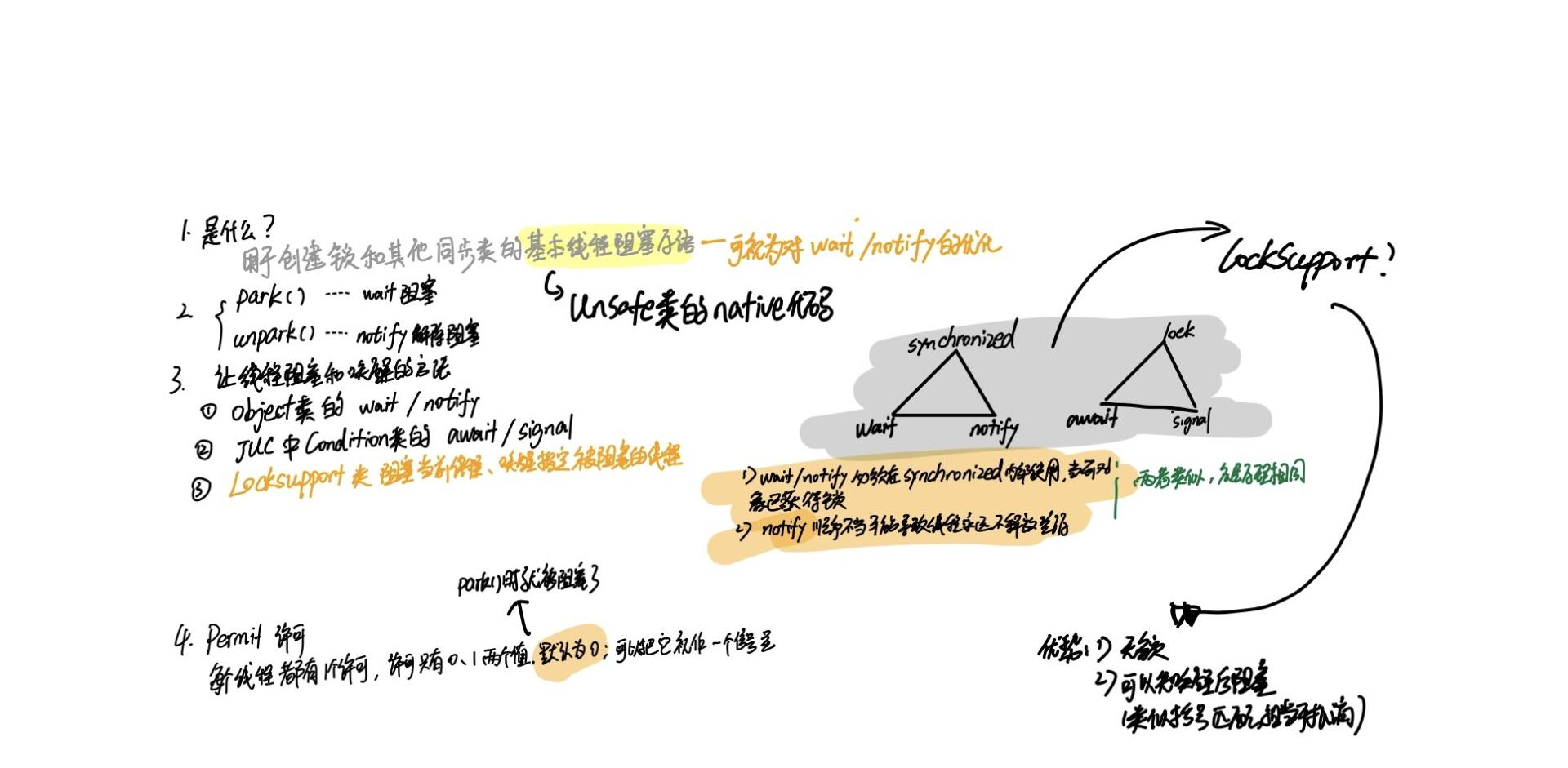
> 贴一个之前的笔记,字迹比较潦草zz 有空的时候这里会补上说明
## 实现1
```java
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
class Main{
static Thread a = null, b=null;
public static void main(String[] args){
a = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1;i<=99;i+=2){
System.out.println(i);
LockSupport.unpark(b);
LockSupport.park();
}
}
});
b = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 2;i<=100;i+=2){
LockSupport.park();
System.out.println(i);
LockSupport.unpark(a);
}
}
});
a.start();
b.start();
}
}
```
## 实现2
```java
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class Main {
static AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(1);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Print p1 = new Print();
Print p2 = new Print();
Thread t1 = new Thread(p1); //t1对应p1任务 但p1任务的线程挂在t2上方便t1唤醒它
Thread t2 = new Thread(p2);
t1.setName("thread-cc-1");
t2.setName("thread-cc-2");
p1.setT(t2);//给p1的Thread设置为t2方便t1唤醒它
p2.setT(t1);
t1.start();
t2.start();
// 唤醒线程t1打印奇数,线程1打印奇数,线程2打印偶数
LockSupport.unpark(t1);
}
static class Print implements Runnable {
private volatile Thread t;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 进入之后立即阻塞
LockSupport.park();
if (num.get() > 100) {
LockSupport.unpark(t);
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + num.getAndIncrement());
// 这里的t实际上是与currentThread不同的另一个线程
// 因此实现了 奇数唤醒偶数线程,偶数唤醒奇数线程
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
}
public void setT(Thread t) {
this.t = t;
}
}
}
```
点评:可拓展性实现2相对较差一些(实现3个线程交替打印etc)
# Synchronized + wait/notify实现
```java
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
MyPrint print = new MyPrint();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(print,"A");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(print,"B");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class MyPrint implements Runnable{
int i = 1;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
synchronized (this){
this.notify();//在这里唤醒的目的是为保证拿到锁的线程只有一个
// 不会立即释放锁 退出代码块才会释放锁
if (i <= 100){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i++);
}else {
return;
}
try {
this.wait();//打印过数据的线程等待 必须等到没打印过数字的拿到锁了才能唤醒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
```
# Lock搭配Condition实现
```java
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// 使用ReentrantLock的newCondition()方法创建三个Condition
// 分别对应A、B、C三个线程
Condition conditionA = lock.newCondition();
Condition conditionB = lock.newCondition();
// A线程
new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lock();
for (int i = 1; i <= 99; i+=2) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" " + i);
// 叫醒B线程
conditionB.signal();
// 本线程阻塞
conditionA.await();
}
// 这里有个坑,要记得在循环之后调用signal(),否则线程可能会一直处于
// wait状态,导致程序无法结束
conditionB.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 在finally代码块调用unlock方法
lock.unlock();
}
}, "A").start();
// B线程
new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lock();
for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i+=2) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +" " + i);
conditionA.signal();
conditionB.await();
}
conditionA.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "B").start();
}
}
```
# Semaphore
```java
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化许可数为1,A线程可以先执行
Semaphore semaphoreA = new Semaphore(1);
// 初始化许可数为0,B线程阻塞
Semaphore semaphoreB = new Semaphore(0);
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 99; i+=2) {
try {
// A线程获得许可,同时semaphoreA的许可数减为0,进入下一次循环时
// A线程会阻塞,知道其他线程执行semaphoreA.release();
semaphoreA.acquire();
// 打印当前线程名称
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
// semaphoreB许可数加1
semaphoreB.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i+= 2) {
try {
semaphoreB.acquire();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " " + i);
semaphoreA.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "B").start();
}
}
```

多线程交替打印奇偶数

![LeetCode1114. 按序打印[多线程] 6种解法](https://i.loli.net/2021/04/20/klrjqHUDgdCx4p6.png)